Resources
Greenhouse Gas Protocols
The process of measuring an organization’s carbon emissions is defined by the framework for carbon accounting – The Greehouse Gas Protocol (GHGP). This ensures that your calculations and reporting is in line with a standardized framework. Accuracy is depended on first defining the organizational and operational boundaries of carbon measurements.
Organisational Boundaries
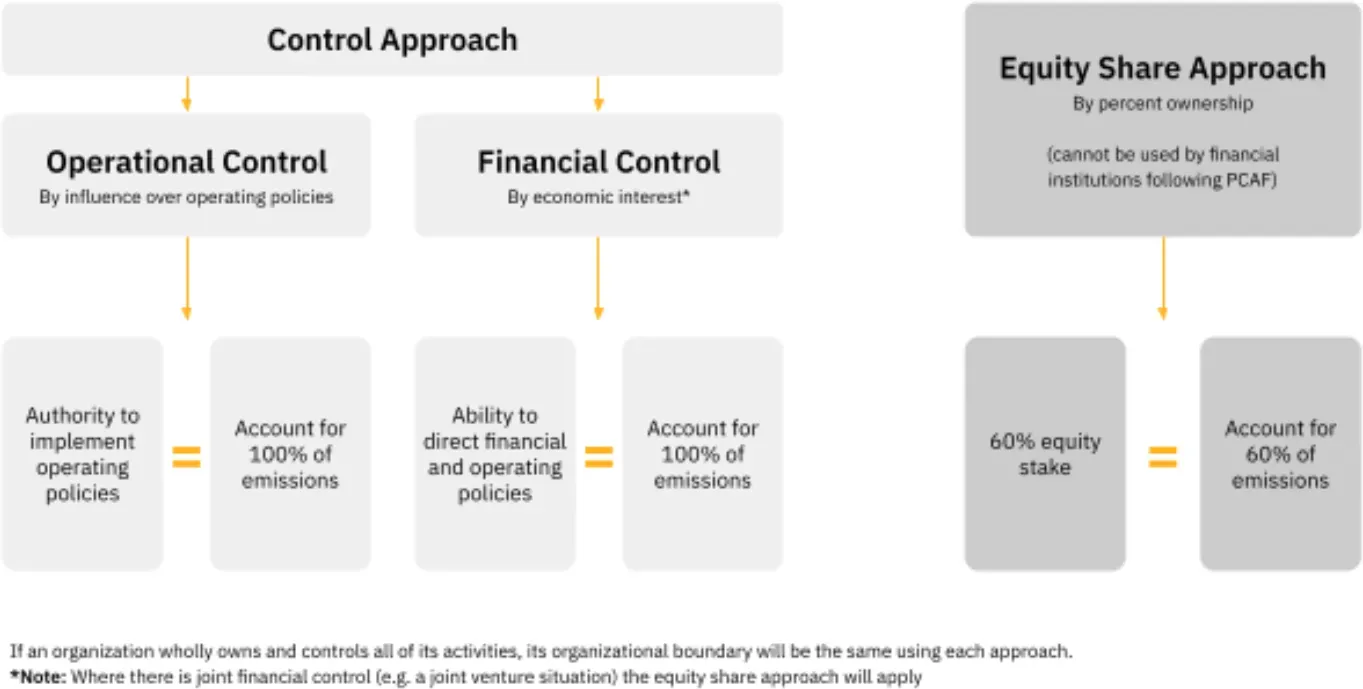
An organizational boundary is an essential framework, dictating the extent of control an organization has over the emissions produced within its operations. The primary methods for defining organizational boundaries are the equity share approach and the control approach.
Equity Share Approach
The equity share approach is a technique employed to ascertain an organization's responsibility for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, contingent upon its ownership interest or equity share in other entities. The emissions attributed to an organization are calculated in accordance with its ownership proportion or controlling interest in affiliated companies or subsidiaries.
Control Approach
Under the control approach, a company is responsible for 100% of the emissions over which it has either financial control or operational control.
Financial Control
A company falls within the financial control boundary if it bears the majority of risks and benefits associated with owning the assets of the operation and exercises overarching control over financial policies. This designation does not inherently imply that the company holds a majority ownership stake in an organization.
Operational Control
The operational control boundary is applied when an organization or one of its subsidiaries exercises complete authority over the day-to-day operational policies of a company.
Operational Boundaries
These boundaries distinguish between emissions directly generated by the organization (direct emissions) and those stemming indirectly from activities within the organization but taking place at sources outside its jurisdiction (indirect emissions). Operational boundaries aid companies in identifying, measuring, and addressing their carbon footprint across different emission sources within their business operations and value chains.
Direct and indirect emissions are broken down into Scope 1, 2, and 3, per the GHGP:
- Scope 1 refers to the direct emissions from an organization's operations, including company vehicles and buildings.
- Scope 2 categorizes indirect emissions from purchased electricity, heating, and cooling.
- Scope 3 comprises all other indirect emissions that exist in a company's value chain, such as upstream material collections or downstream product use.
Regulatory Climate Policies
Contact us to discuss how any of these climate policies can impact and create value for your business operations.
United States
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Climate Disclosure Rule for Public Companies
- California Senate Bill 253 (SB253)
- California Senate Bill 261 (SB261)
European Union
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)
- Proposal for a directive on empowering consumers for the green transition
- Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
United Kingdom
- UK Sustainability Disclosure Standards
- Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) Regulation
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) Listing Standards
Canada
- Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) Guidance
International
- International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB)
- Task Force on Climate Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
- The Value Reporting Foundation’s (VRF) Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
- The Global GHG Accounting and Reporting Standard for the Financial Industry
Adding Corporate Value
Enhance your corporate value in several ways:

1. Cost Savings
Implementing energy-efficient practices, optimizing resource usage, and adopting renewable energy sources can lead to significant cost savings over time. Reduced energy consumption and waste not only lower operational expenses but also improve overall efficiency.

2. Brand Reputation
Demonstrating environmental responsibility and sustainability can enhance your brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental issues and are more likely to support companies that actively work to reduce their carbon footprint. A positive brand image can attract customers, strengthen customer loyalty, and differentiate your organization from competitors.

3. Regulatory Compliance
Many governments are implementing stricter environmental regulations to combat climate change. Proactively reducing your carbon footprint can help ensure compliance with current and future regulations, avoiding potential fines, penalties, and legal risks.
4. Risk Mitigation
Climate change poses various risks to businesses, including supply chain disruptions, extreme weather events, and regulatory changes. By reducing your carbon footprint and transitioning to sustainable practices, you can mitigate these risks and build resilience against future challenges.
5. Access to Capital
Investors are increasingly considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors when making investment decisions. Companies with strong sustainability initiatives and a low carbon footprint may attract more investment capital and access to favorable financing terms.
6. Employee Engagement and Retention
Embracing sustainability initiatives can improve employee morale, engagement, and retention. Employees are often more motivated and proud to work for organizations that prioritize environmental responsibility and contribute to positive social impact.
7. Innovation and Market Opportunities
Pursuing carbon footprint reduction initiatives can drive innovation within your organization. Developing and offering sustainable products and services can open up new market opportunities and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
1. Cost Savings
Implementing energy-efficient practices, optimizing resource usage, and adopting renewable energy sources can lead to significant cost savings over time. Reduced energy consumption and waste not only lower operational expenses but also improve overall efficiency.
2. Brand Reputation
Demonstrating environmental responsibility and sustainability can enhance your brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental issues and are more likely to support companies that actively work to reduce their carbon footprint. A positive brand image can attract customers, strengthen customer loyalty, and differentiate your organization from competitors.
The Impact of No Strategy

Damages Corporate Reputation
The reputational value of the corporate brand is affected by business response to regulatory evolution.

Reduces Product Market Share
The non-compliance, lack of accountability and weak sustainability messaging will impact market share and business continuity.

Decreases Business Valuation
As greater transparency is demanded on the disclosure of climate change risks and opportunities, this will impact fair value measurement of assets and liabilities.

Limits Financial Instruments
Climate related matters may affect the ability to satisfy conditions for loans, insurance coverage and can affect estimates of future taxable profits, cash flow and the value of collateral.
Overcoming The Hurdles
The biggest barrier to participating in carbon accounting is the accurate calculation of data.
Granularity is necessary to identify your carbon hotspots and develop targeted mitigation strategies.
The integrated services and expertise at Blewcoast assure a pragmatic and sustainable solution to overcoming these hurdles.
Schedule A Call
Contact us for a no-obligation conversation and discover how your business can benefit from partnering with Blewcoast.
All Rights Reserved | BLEWSTREAM Ecosystem
